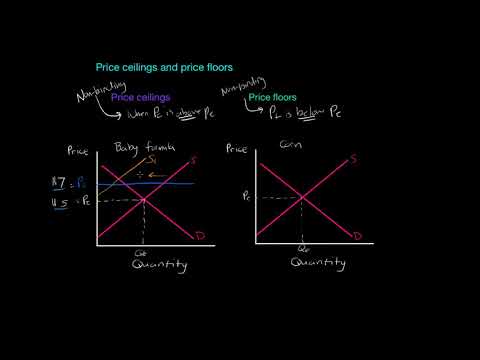
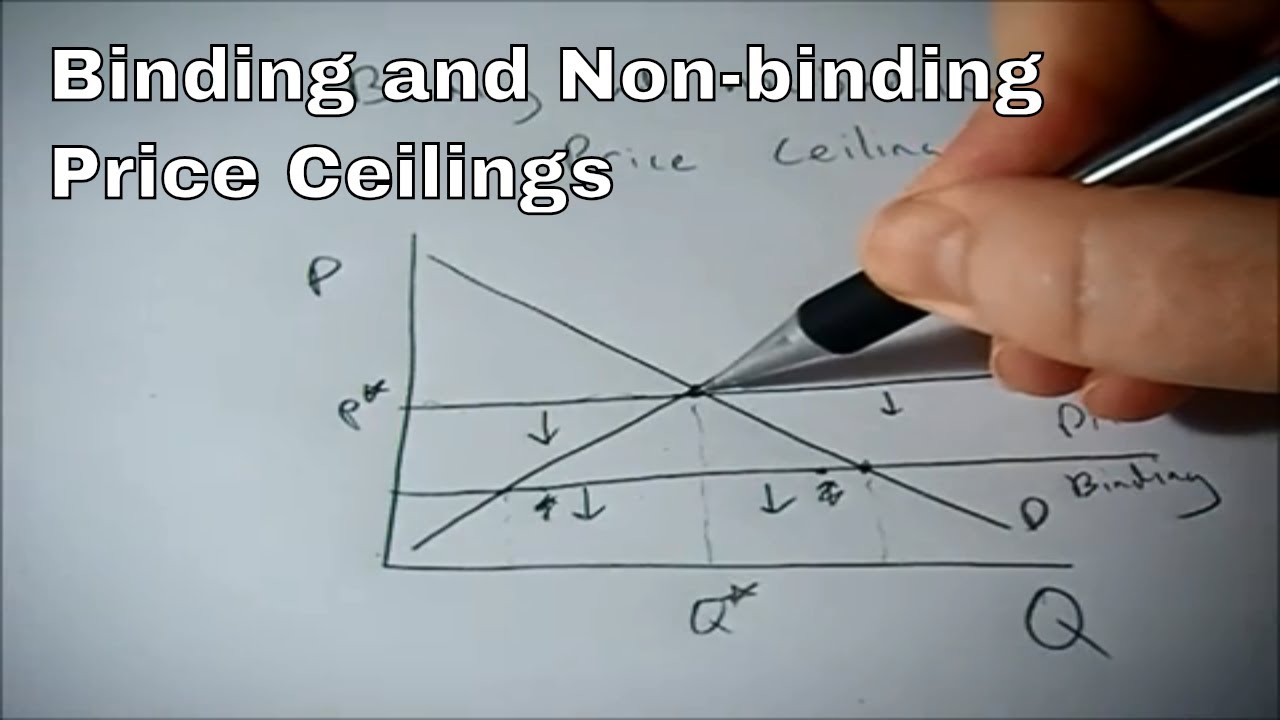
In general a price ceiling will be non binding whenever the level of the price ceiling is greater than or equal to the equilibrium price that would prevail in an unregulated market.
A nonbinding price floor is shown in.
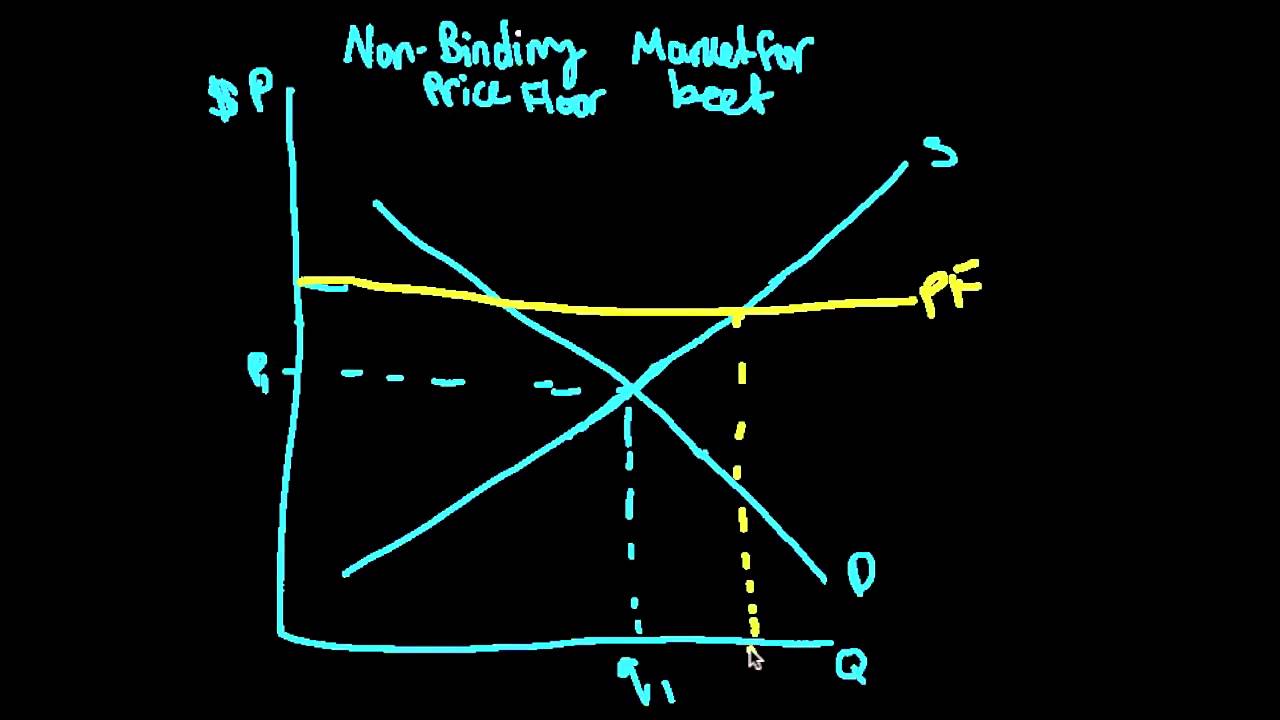
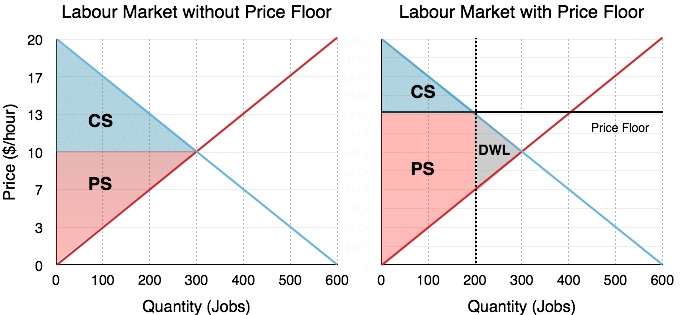
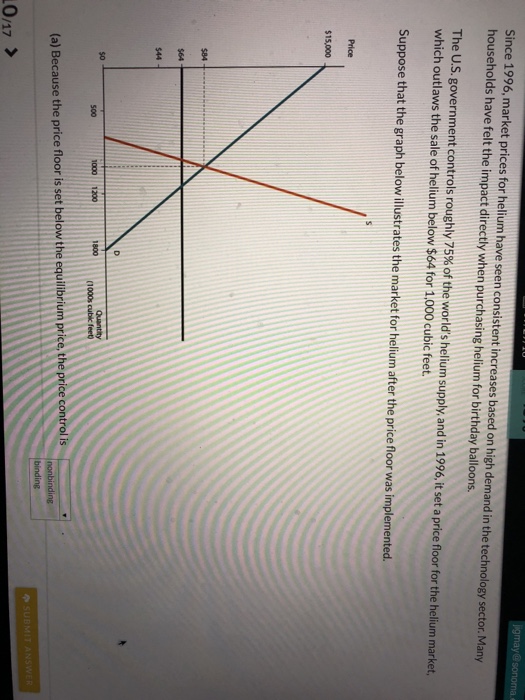
The government establishes a price floor of pf.
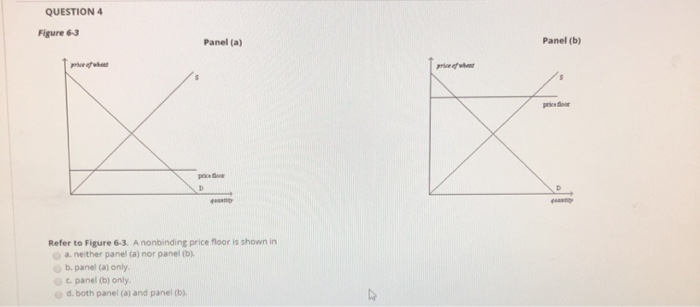
Panel a only oc panel b only.
For competitive markets like the one shown above we can say that a price ceiling is non binding when pc p.
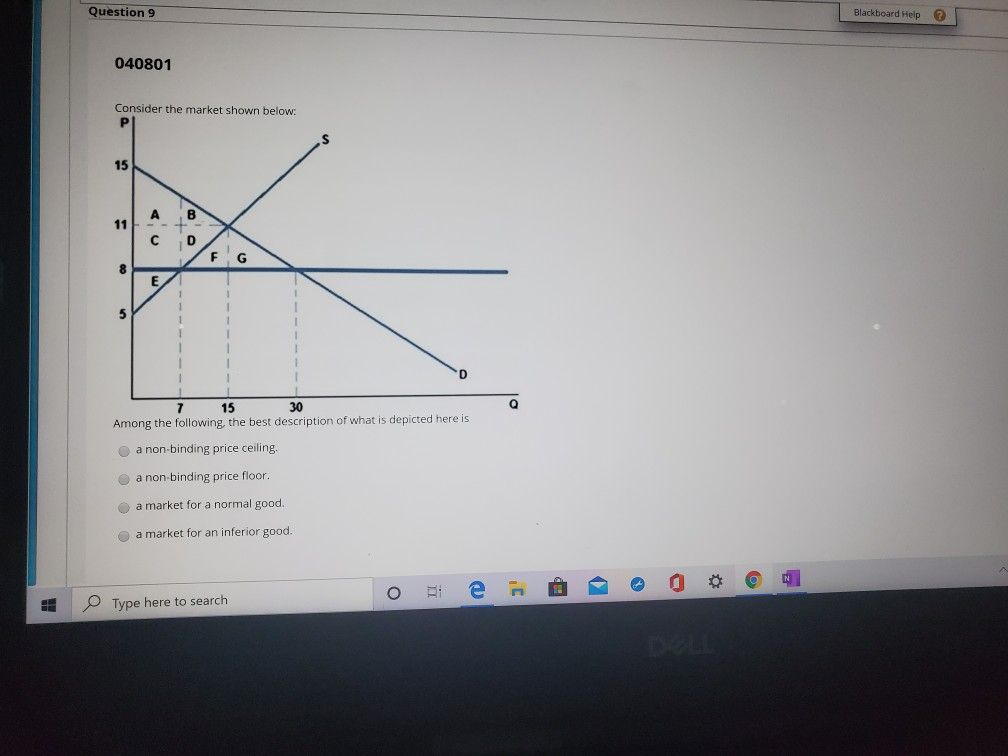
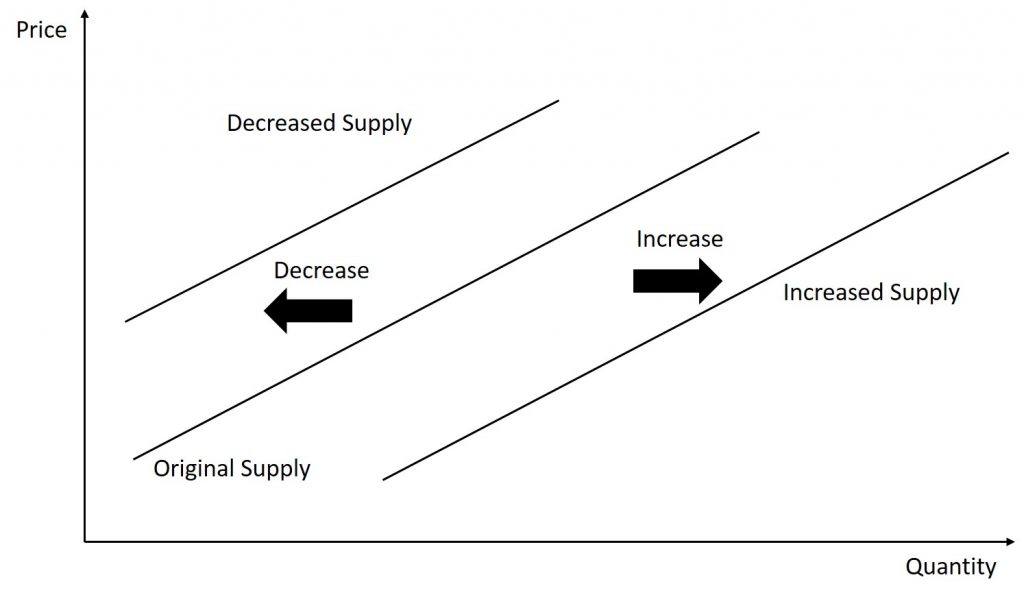
Consider the figure below.
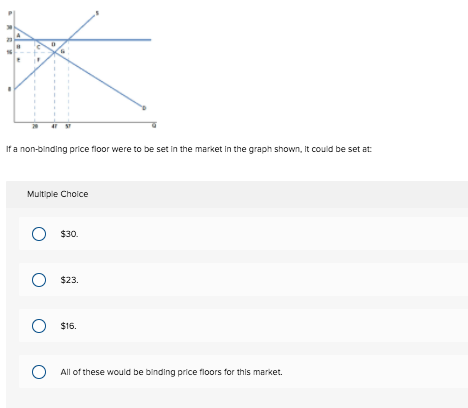
A non binding price floor is shown in.
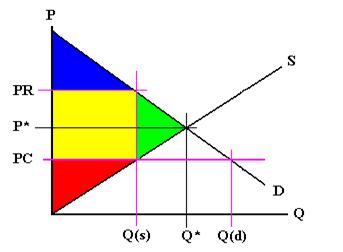
At the price p the consumers demand for the commodity equals the producers supply of the commodity.
Note that the price floor is below the equilibrium price so that anything price above the floor is feasible.
The equilibrium market price is p and the equilibrium market quantity is q.
If a price ceiling is not binding then.
The equilibrium price is below the price ceiling.
In panel b there will be.
Refer to figure 6 3.
The latter example would be a binding price floor while the former would not be binding.
Another way to think about this is to start at a price of 100 and go down until you the price floor price or the equilibrium price.
Both panel a and panel b get more help from chegg.
Refer to figure 6 3.
Get 1 1 help now from expert economics tutors.
Question 4 figure 6 3 panel b panel a price of wh price ofh pric or refer to figure 6 3.
This video explains and shows how a non binding price floor becomes ineffective.